Research
I am passionate about enabling autonomous robots to safely navigate and interact in complex environments. My research focuses on 3D scene representation learning, vision-language models for robotics, and robot task planning with large language models. I leverage CUDA, C++, Python etc. to develop algorithms that allow robots to perceive, reason, and act in the real world.
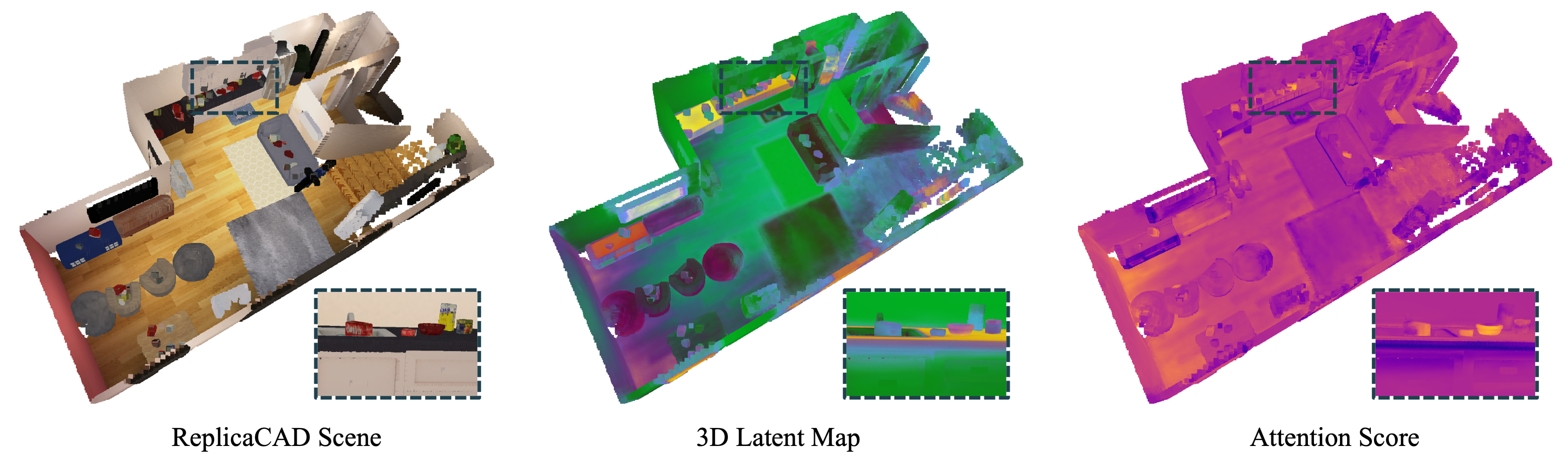
Seeing the Bigger Picture: 3D Latent Mapping for Mobile Manipulation Policy Learning
We develop Seeing the Bigger Picture (SBP), an end-to-end policy learning approach that operates directly on a 3D map of latent features. In SBP, the map extends perception beyond the robot's current field of view and aggregates observations over long horizons, which achieves stronger spatial and temporal reasoning than policies relying solely on images.
ICRA 2026
Best Paper Nomination @ RoboReps Workshop RSS 2025
LTLCodeGen: Code Generation of Syntactically Correct Temporal Logic for Robot Task Planning
We develop LTLCodeGen, a method that uses large language model (LLM) code generation to translate natural language robot navigation instructions into syntactically correct linear temporal logic (LTL) formulas that can be combined with a semantic occupancy map to generate robot trajectories satisfying the specified tasks.
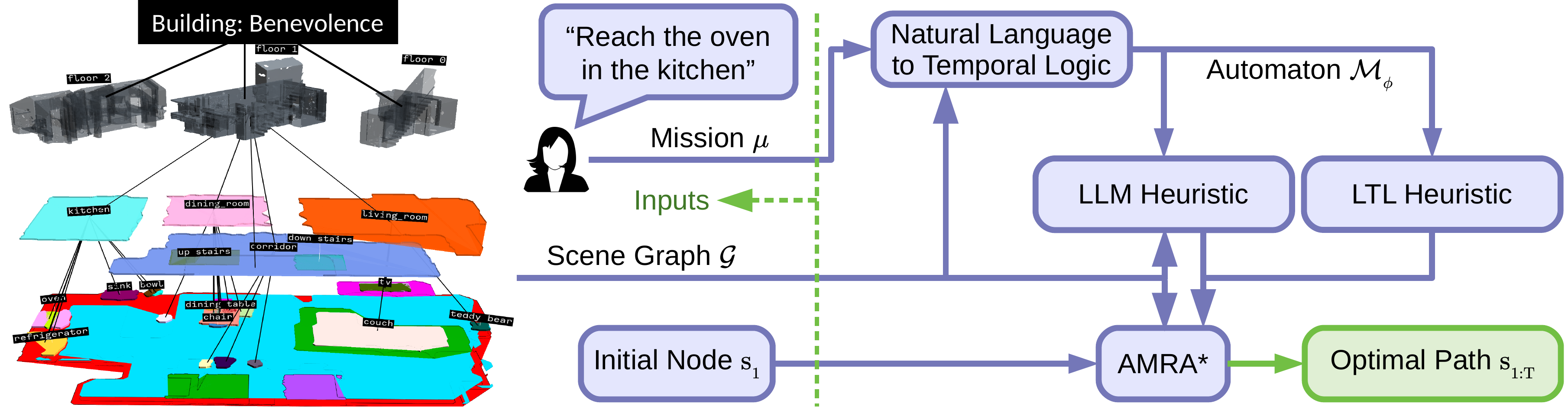
Optimal Scene Graph Planning with Large Language Model Guidance
Our work enables optimal hierarchical LTL planning with LLM guidance over scene graphs. To achieve efficiency, we construct a hierarchical planning domain that captures the attributes and connectivity of the scene graph and the task automaton, and provide semantic guidance via an LLM heuristic function. To guarantee optimality, we design an LTL heuristic function that is provably consistent and supplements the potentially inadmissible LLM guidance in multi-heuristic planning.

Learning Scene-Level Signed Directional Distance Function for Aerial Autonomy
We propose Signed Directional Distance Function (SDDF), a novel 3D scene representation that encodes the signed distance from a position to the nearest surface along a direction. SDDF enhances geometry modeling, occlusion capture, collision checking and differentiable view prediction for trajectory optimization of aerial robots.
Best Paper Award @ Workshop on Leveraging Implicit Methods for Aerial Autonomy at RSS 2025
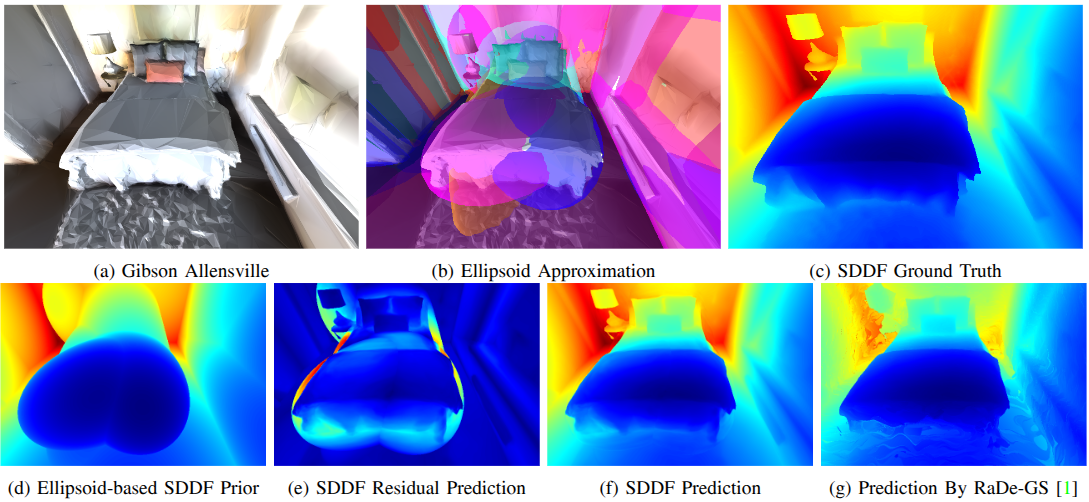
Learning Scene-Level Signed Directional Distance Function with Ellipsoidal Priors and Neural Residuals
To learn and predict scene-level SDDF efficiently, we develop a differentiable hybrid representation that combines explicit ellipsoid priors with implicit neural residuals. This approach allows the model to effectively handle large distance discontinuities around obstacle boundaries while preserving the ability for dense, high-fidelity prediction.
Best Paper Award @ Workshop on Leveraging Implicit Methods for Aerial Autonomy at RSS 2025

$\nabla$-SDF: Learning Euclidean Signed Distance Functions Online with Gradient-Augmented Octree Interpolation and Neural Residual
We propose $\nabla$-SDF, a novel 3D scene representation that combines gradient-augmented octree interpolation with a neural residual to learn accurate signed distance functions online in real-time. $\nabla$-SDF outperforms the SOTA neural SDF methods in SDF prediction accuracy.
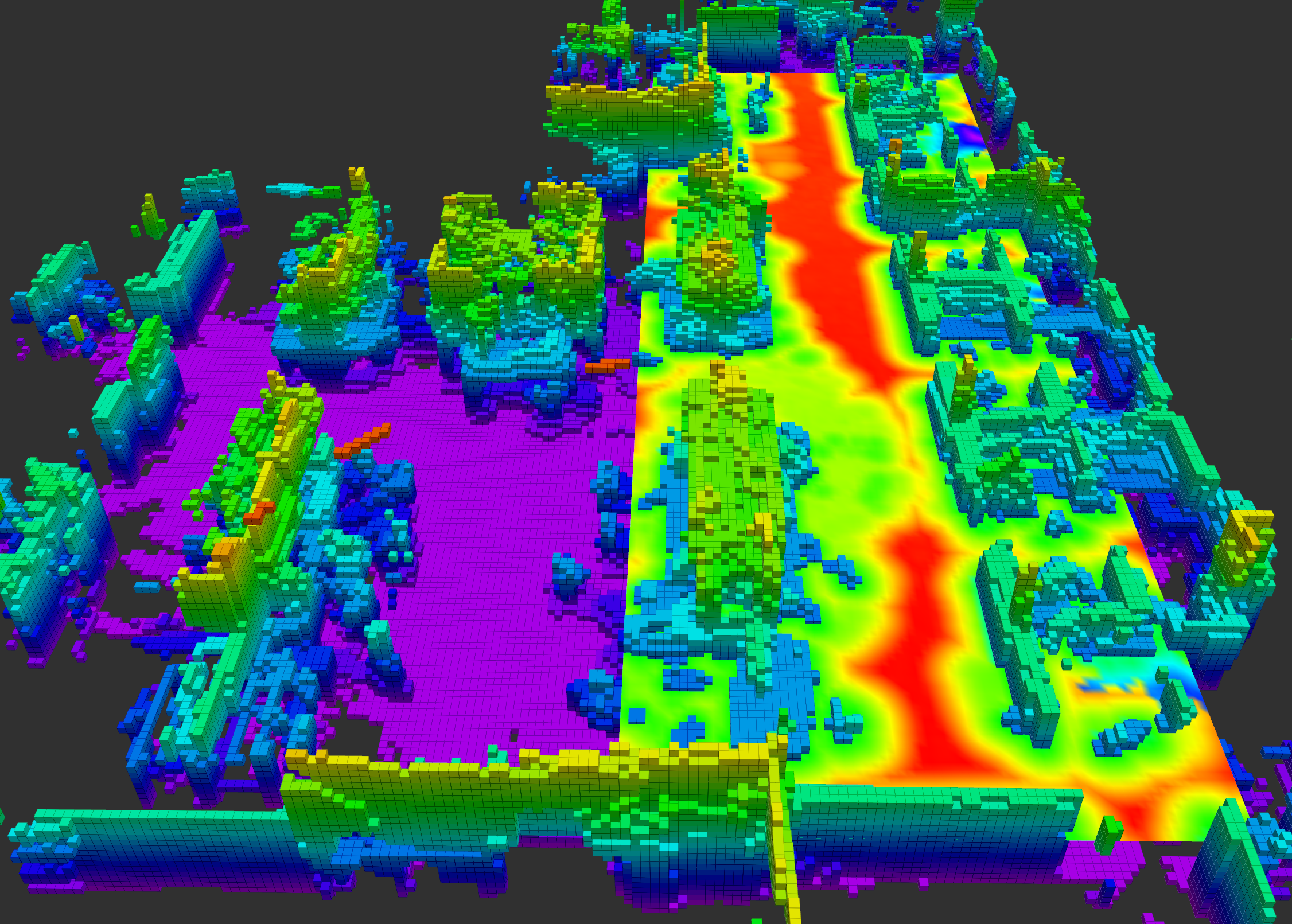
Real-Time Learning of Signed Distance Function via Kernel Regression with Uncertainty Quantification
We develop Kernel-SDF, an open-source library for real-time signed distance function estimation using kernel regression. Kernel-SDF achieves superior accuracy compared to existing methods and outstanding real-time performance, making it suitable for various robotic applications requiring reliable environment representation with uncertainty awareness.
Distributionally Robust Control for Safe Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments
We formulate distributionally robust control barrier functions (DR-CBFs) to incorporate noisy sensor measurements directly into optimization-based control synthesis, guaranteeing safe and efficient autonomous navigation in dynamic environments.